- 线程可以提高程序的执行效率
- Java中只有这么一种东西代表线程(Thread)
- start方法才能并发执行
- 方法栈是线程私有的(局部变量)
- 静态变量/类变量是被所有线程共享的
- 对于
IO密集型场景及其有用
- 对于
CPU密集型稍有折扣(说白了就是不太适用)
- 因为我们多线程的目的本来就是想不让
CPU闲着,闲着CPU已经在密集运算了,因此提升空间不大
- 性能提升的上线
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread is run...");
}
}).start();
System.out.println("Main is run...");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is run...");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).run(); // run 方法会等待当前线程执行结束后才会执行下面的操作
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is run...");
}
}).start(); // start方法才能并发执行
System.out.println("Main is run...");
}
}
|
线程难的本质原因是:你要看着同一份代码,想象不同的人在疯狂以乱序执行它
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public class Main {
private static int i = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
new Thread(Main::modifySharedVariable).start(); // 这也是一种简化写法,叫做方法引用,貌似是Java8 + 引入的特性
}
/*
i = 8
i = 8
i = 8
i = 8
i = 11
i = 21
i = 21
i = 21
...
从上面可以看出,有些数被+了多次,并不是按照我们想象的每次给i+1,这是为什么呢?
那是因为i++不是原子操作,假如现在i=0,多个线程同时获得了执行权,这时候他们拿
到的i的值都是0,因此才发生了上面的情况,某个值被打印了多次
*/
}
public static void modifySharedVariable() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i++;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
public class Main {
private static final Map<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(Main::putIfAbsent).start();
}
/*
Put 0
Put 0
Put 1
Put 6
Put 5
Put 9
Put 8
Put 3
Put 4
Put 2
Put 7
可以看到,0被添加了多次,这是为什么呢?,请看下面截图
*/
}
/**
* 生成一个1到10的随机数,看看map中是否存在这个数,如果不存在则添加进去
* 我们的期望是每个数只可能添加1次
*/
public static void putIfAbsent() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int rNumber = new Random().nextInt(10);
if (!hashMap.containsKey(rNumber)) {
hashMap.put(rNumber, rNumber);
System.out.println("Put " + rNumber);
}
}
}
|
说白了,某个线程获得了执行权,此时它判断map中没有0,于是它准备向map中添加0,但好巧不巧,CPU此时将执行权给了另一个线程,此时它也判断map中没有0,于是它向map中添加了一个0,等到,之前的线程获得了执行权的时候,它继续之前没有完成的操作,向map中添加了0,因此0被向map中,添加了两次,这就是这个问题的原因
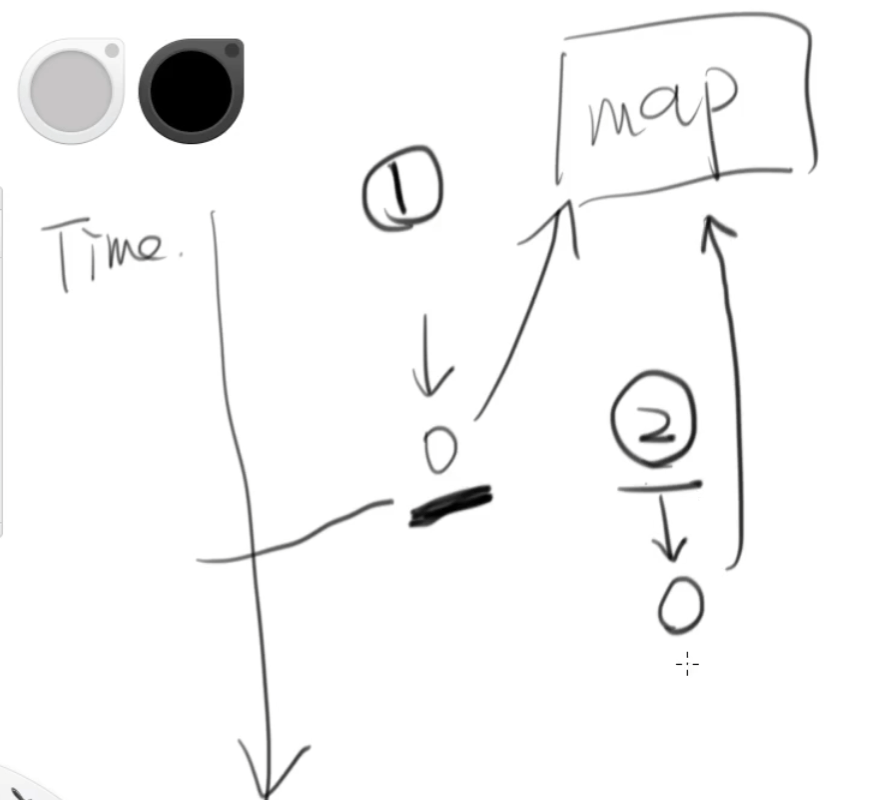
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
public class Main {
// 一般来说new Object都是用来当成锁用的
private static final Object lock1 = new Object(); // Java中任何对象都可以当成锁
private static final Object lock2 = new Object(); // Java中任何对象都可以当成锁
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread1().start();
new Thread2().start();
/*
运行这个程序就被卡主了,这是为什么? 请看下面截图
*/
}
/**
* 创建线程的第二种方式,继承Thread类,重写run方法
*/
static class Thread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
/*
synchronized 语句表示同步,说白了就是获取锁
只有获取到锁的线程才能执行里面的代码
*/
synchronized (lock1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 获取锁2
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 创建线程的第二种方式,继承Thread类,重写run方法
*/
static class Thread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock2) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
}
}
|
线程1,先拿到了锁1,然后休眠500毫秒,线程2,先拿到锁2,然后休眠100毫秒,线程2先醒过来,此时它想要获得锁1,而锁1正被线程1拿到,因此它只能进入等待,此时线程1醒来,它想要获得锁2,但锁2此时正被线程2拿着,于是它也只,进入等待,此时,两个线程都等待在那了,因此进入了所谓的死锁状态
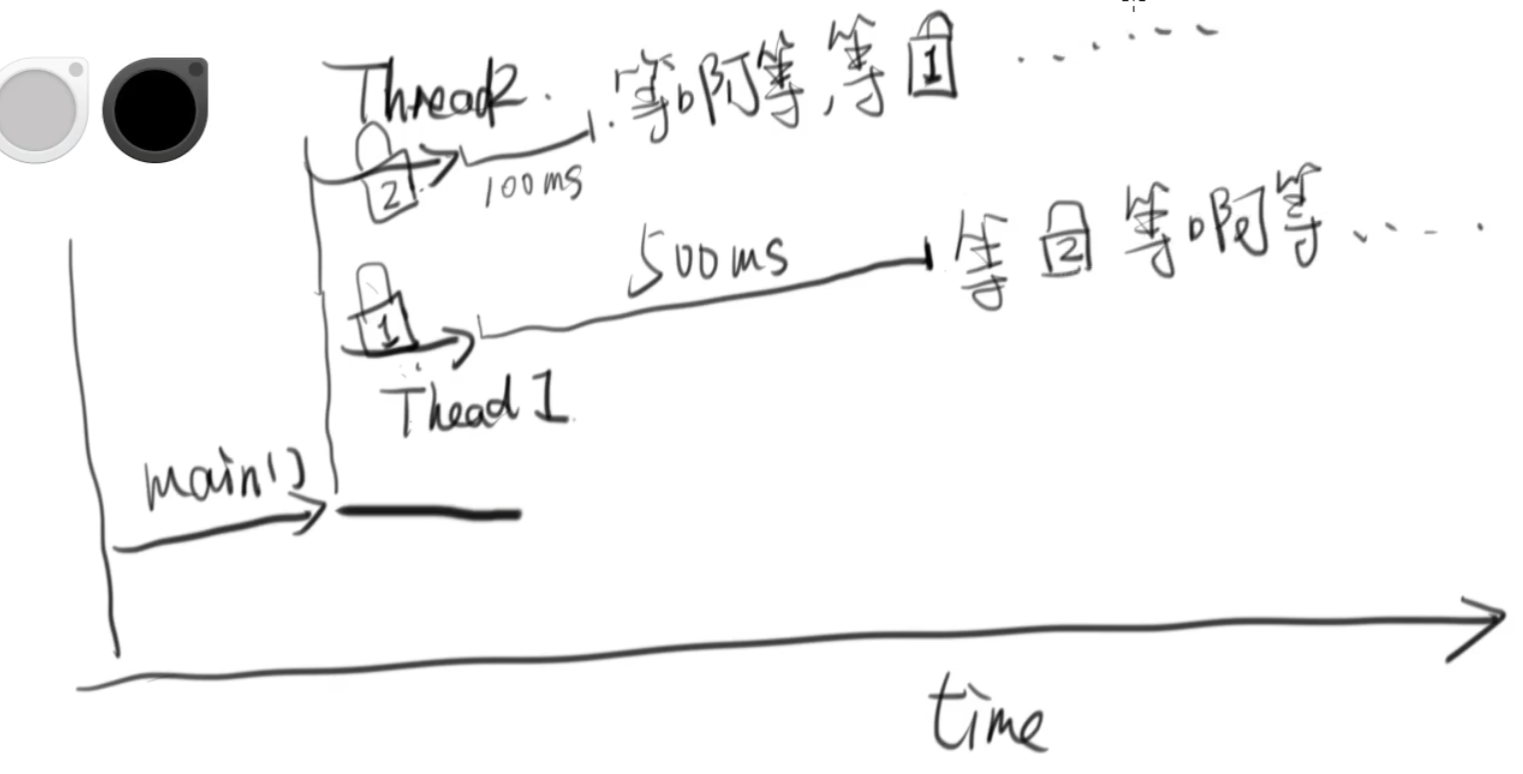
- 先用
jps查找到发生死锁的进程id
- 再用
jstack查看该进程的堆栈
所有线程都按照相同的顺序获得资源锁
上例代码产生死锁的原因就是,线程1先获得锁1,再获得锁2,线程2先获得锁2,再获得锁1
利用synchronized解决例子1中的问题
synchronized 锁住的是指定的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public class Main {
private static int i = 0;
private static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
new Thread(Main::modifySharedVariable).start();
}
}
public static void modifySharedVariable() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock) {
i += 1;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}
|
synchronized 静态方法锁住的是Class对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class Main {
private static int i = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
new Thread(Main::modifySharedVariable).start();
}
}
public synchronized static void modifySharedVariable() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i += 1;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
|
synchronized 实例方法锁住的是this
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
public class Main {
private static int i = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
Main main = new Main();
new Thread(main::modifySharedVariable).start();
}
}
public synchronized void modifySharedVariable() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i += 1;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
// 这个方法等价于上面的方法
public void modifySharedVariable2() {
synchronized (this) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i += 1;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}
|
它可以将集合转换成线程安全的
- ArrayList
- HashSet
- TreeSet
- HashMap
- LinkedHashMap
- ....
- ConcurrentHashMap
- AtomicBoolean
- AtomicLong
- AtomicInteger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class Main {
private static final AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
new Thread(Main::modifySharedVariable).start();
}
}
public static void modifySharedVariable() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(i.addAndGet(1));
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public class Main {
private static int i = 0;
private static final ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
new Thread(Main::modifySharedVariable).start();
}
}
public static void modifySharedVariable() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
reentrantLock.lock();
i += 1;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
|
当前线程将进入等待,并释放锁,直到另一个线程调用notify或notifyAll方法
唤醒等待中的线程,如果有多个线程同时在等待,那么将会随机挑选一个唤醒
唤醒所有等待中的线程,唤醒后,它们将重新竞争锁,这个竞争是没有特权的,
和平常一样,谁运气好,谁就能获得锁,没能获得锁的线程,将重新陷入等待
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
|
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Random;
public class ProducerConsumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Container container = new Container();
Object o = new Object();
Producer producer = new Producer(container, o);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(container, o);
producer.start();
consumer.start();
producer.join();
producer.join();
}
public static class Producer extends Thread {
private final Container container;
private final Object lock;
public Producer(Container container, Object lock) {
this.container = container;
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (container.getValue().isPresent()) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int r = new Random().nextInt();
System.out.println("Producing " + r);
container.setValue(Optional.of(r));
lock.notify();
}
}
}
}
public static class Consumer extends Thread {
private final Container container;
private final Object lock;
public Consumer(Container container, Object lock) {
this.container = container;
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (!container.getValue().isPresent()) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Consuming " + container.getValue().get());
container.setValue(Optional.empty());
lock.notify();
}
}
}
}
private static class Container {
public Optional<Integer> getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Optional<Integer> value) {
this.value = value;
}
private Optional<Integer> value = Optional.empty();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
|
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class ProducerConsumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Container container = new Container();
ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition isProduce = reentrantLock.newCondition();
Condition isConsume = reentrantLock.newCondition();
Producer producer = new Producer(container, reentrantLock, isProduce, isConsume);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(container, reentrantLock, isProduce, isConsume);
producer.start();
consumer.start();
producer.join();
producer.join();
}
public static class Producer extends Thread {
private final Container container;
private final ReentrantLock reentrantLock;
private final Condition isProduce;
private final Condition isConsume;
public Producer(Container container, ReentrantLock reentrantLock, Condition isProduce, Condition isConsume) {
this.container = container;
this.reentrantLock = reentrantLock;
this.isProduce = isProduce;
this.isConsume = isConsume;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
reentrantLock.lock();
if (container.getValue().isPresent()) {
try {
isProduce.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int r = new Random().nextInt();
System.out.println("Producing " + r);
container.setValue(Optional.of(r));
isConsume.signal();
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static class Consumer extends Thread {
private final Container container;
private final ReentrantLock reentrantLock;
private final Condition isProduce;
private final Condition isConsume;
public Consumer(Container container, ReentrantLock reentrantLock, Condition isProduce, Condition isConsume) {
this.container = container;
this.reentrantLock = reentrantLock;
this.isProduce = isProduce;
this.isConsume = isConsume;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
reentrantLock.lock();
if (!container.getValue().isPresent()) {
try {
isConsume.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Consuming " + container.getValue().get());
container.setValue(Optional.empty());
isProduce.signal();
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}
private static class Container {
public Optional<Integer> getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Optional<Integer> value) {
this.value = value;
}
private Optional<Integer> value = Optional.empty();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class ProducerConsumer3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1);
BlockingQueue<Integer> single = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1);
Producer producer = new Producer(blockingQueue, single);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(blockingQueue, single);
producer.start();
consumer.start();
producer.join();
producer.join();
}
public static class Producer extends Thread {
BlockingQueue<Integer> container;
BlockingQueue<Integer> single;
public Producer(BlockingQueue<Integer> container, BlockingQueue<Integer> single) {
this.container = container;
this.single = single;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int r = new Random().nextInt();
System.out.println("Producing " + r);
try {
container.put(r);
single.take(); // 等待Consumer通知我再生产
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static class Consumer extends Thread {
BlockingQueue<Integer> container;
BlockingQueue<Integer> single;
public Consumer(BlockingQueue<Integer> container, BlockingQueue<Integer> single) {
this.container = container;
this.single = single;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("Consuming " + container.take());
single.put(0); // 通知Producer再次生产
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
public class ProducerConsumer4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Container container = new Container();
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1, true); // 创建公平锁,当两个线程同时具备竞争锁的条件时,一人一次
Producer producer = new Producer(container, semaphore);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(container, semaphore);
producer.start();
consumer.start();
producer.join();
producer.join();
}
public static class Producer extends Thread {
private final Container container;
private final Semaphore semaphore;
public Producer(Container container, Semaphore semaphore) {
this.container = container;
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
if (!container.getValue().isPresent()) {
int r = new Random().nextInt();
System.out.println("Producing " + r);
container.setValue(Optional.of(r));
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
}
public static class Consumer extends Thread {
private final Container container;
private final Semaphore semaphore;
public Consumer(Container container, Semaphore semaphore) {
this.container = container;
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
if (container.getValue().isPresent()) {
System.out.println("Consuming " + container.getValue().get());
container.setValue(Optional.empty());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
}
private static class Container {
public Optional<Integer> getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Optional<Integer> value) {
this.value = value;
}
private Optional<Integer> value = Optional.empty();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
public class ProducerConsumer5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Exchanger<Optional<Integer>> exchanger = new Exchanger<>();
Exchanger<Boolean> single = new Exchanger<>();
Producer producer = new Producer(exchanger, single);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(exchanger, single);
producer.start();
consumer.start();
producer.join();
producer.join();
}
public static class Producer extends Thread {
Optional<Integer> container = Optional.empty();
Exchanger<Optional<Integer>> exchanger;
Exchanger<Boolean> single;
public Producer(Exchanger<Optional<Integer>> exchanger, Exchanger<Boolean> single) {
this.exchanger = exchanger;
this.single = single;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (!container.isPresent()) {
int r = new Random().nextInt();
System.out.println("Producing " + r);
container = Optional.of(r);
}
try {
container = exchanger.exchange(container); // 交换容器,如果对方没有到达交换点则阻塞
single.exchange(true);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static class Consumer extends Thread {
Optional<Integer> container = Optional.empty();
Exchanger<Optional<Integer>> exchanger;
Exchanger<Boolean> single;
public Consumer(Exchanger<Optional<Integer>> exchanger, Exchanger<Boolean> single) {
this.exchanger = exchanger;
this.single = single;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
container = exchanger.exchange(container); // 交换容器,如果对方没有到达交换点则阻塞
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (container.isPresent()) {
System.out.println("Consuming " + container.get());
container = Optional.empty();
try {
single.exchange(false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
- 线程池是预先定义好的若干个线程
- Java中线程池的实现是通过
Executors
Runable和Callable
Runable 没有返回值Runable 没有声明抛出的异常(这意味着你要实现它的话,必须把异常吞掉,这是非常不爽的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
/*
* return Future 表示一个未来才会有结果的东西
*/
Future<Integer> future1 = threadPool.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return 0;
}
});
/*
* return Future 表示一个未来才会有结果的东西
*/
Future<String> future2 = threadPool.submit(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "Hello Thread.";
}
});
/*
* return Future 表示一个未来才会有结果的东西
*/
Future<Object> future3 = threadPool.submit(new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return new RuntimeException();
}
});
// 当调用get方法时,如果结果还没有被返回,则会阻塞
System.out.println(future1.get());
System.out.println(future2.get());
System.out.println(future3.get());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class MultiThreadWordCount1 {
/*
使用threadNum个线程,并发统计文件中各单词的数量
*/
public static Map<String, Integer> count(int threadNum, List<File> files) throws FileNotFoundException,
ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadNum);
Map<String, Integer> finalResult = new HashMap<>();
for (File file : files) {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
List<Future<Map<String, Integer>>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
futures.add(threadPool.submit(new Worker(bufferedReader)));
}
Map<String, Integer> eachResult = new HashMap<>();
for (Future<Map<String, Integer>> future : futures) {
Map<String, Integer> workResult = future.get();
meargeWorkerResultToFinalResult(workResult, eachResult);
}
meargeWorkerResultToFinalResult(eachResult, finalResult);
}
return finalResult;
}
private static void meargeWorkerResultToFinalResult(Map<String, Integer> workResult,
Map<String, Integer> finalResult) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : workResult.entrySet()) {
int count = finalResult.getOrDefault(entry.getKey(), 0) + entry.getValue();
finalResult.put(entry.getKey(), count);
}
}
static class Worker implements Callable<Map<String, Integer>> {
BufferedReader bufferedReader;
Worker(BufferedReader bufferedReader) {
this.bufferedReader = bufferedReader;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Integer> call() throws Exception {
String line;
Map<String, Integer> result = new HashMap<>();
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] words = line.split(" ");
for (String word : words) {
result.put(word, result.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
}
}
return result;
}
}
}
|

